|
Note
| If you have a token from your Solutions Architect, the installation requirements and preliminary steps are slightly different. See Install with Token and Fleetcommand CLI for details. |
This topic is a basic outline of the Domino installation process.
If you need platform-specific instructions, see the following:
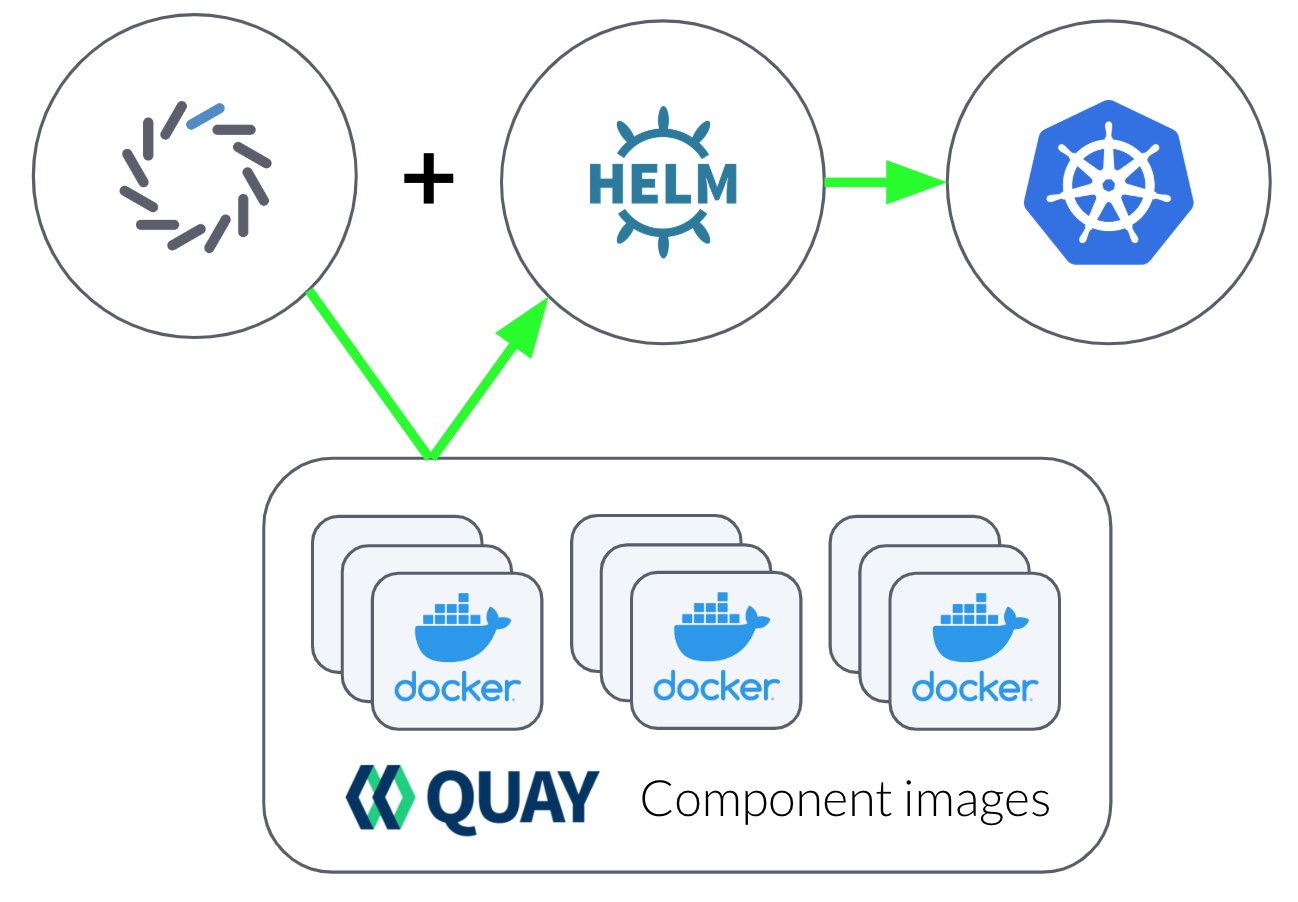
Use fleetcommand-agent to install Domino.
fleetcommand-agent is a Python-based automation tool that runs inside a Docker container.
Since Domino runs on Kubernetes, fleetcommand-agent uses Helm to deploy Domino into a compatible cluster.
You can run fleetcommand-agent locally or as a job in the target cluster.
Domino recommends that you use the streamlined domino.yaml files to complete your Domino install.
These are configuration files that ease the Domino deployment process.
domino.yaml provides a streamlined experience, while domino-full.yaml includes the default fields for advanced configuration.
See Streamlined domino.yaml Downloads for more information and a complete list of downloads for supported Kubernetes distributions and cloud platforms.
The install automation tools are delivered as a Docker image, and must run on an installation workstation that meets the following requirements:
-
Docker installed.
-
Access to download and install Helm through package manager or GitHub.
-
Access to quay.io and credentials for an installation service account with access to the Domino installer image and upstream image repositories. Throughout these instructions, these credentials will be referred to as
$QUAY_USERNAMEand$QUAY_PASSWORD. Contact your Domino account team if you need new credentials.
-
Confirm that your workstation fulfills the installation requirements.
-
If you haven’t done so already, pull the
fleetcommand-agentimage. -
Access the default entrypoint for
fleetcommand-agent:"Entrypoint": [ "python", "-m", "fleetcommand_agent"]This command launches
fleetcommand-agentinside the container at/app/fleetcommand_agent. You can accessfleetcommand-agentand run commands throughdocker run:docker run --rm quay.io/domino/fleetcommand-agent:v58 $COMMAND $ARGUMENTS
|
Important
|
A Domino install can’t be hosted on a subdomain of another Domino install.
For example, if you have Domino deployed at data-science.example.com, you can’t deploy another instance of Domino at acme.data-science.example.com.
|
|
Note
|
The fleetcommand-agent installer requires k8s' cluster-admin role in order to apply all the needed resources. For more information, see kubernetes.io - Using RBAC Authorization.
|
-
Connect to a workstation that meets the installation automation requirements listed previously. You do not have to use an account with root privileges to run the installer.
-
Log in to
quay.iowith the credentials described in the previous requirements section.docker login quay.io
-
Retrieve the Domino installer image from
quay.io.docker pull quay.io/domino/fleetcommand-agent:v58
-
To generate a template configuration file named
domino.yml, initialize the installer.docker run --rm -it -v $(pwd):/install quay.io/domino/fleetcommand-agent:v58 \ init --file /install/domino.yml
-
Edit the configuration file with details about the target cluster, storage systems, and host domain. Read the configuration reference for more information about available keys, and consult the configuration examples for guidance about how to get started.
Update the helm image registry section of your configuration to include your
qauy.iocredentials. -
To install Domino, download the fleetcommand-agent-install.sh script.
-
Run the
fleetcommand-agent-install.shscript from the same directory as the configuration file while specifying the version of Domino you want to install. For example:fleetcommand-agent-install.sh 5.7.0 -
Installation can take up to 30 minutes to fully complete. The installer will output verbose logs and surface any errors it encounters, but it can also be useful to follow along in another terminal tab by running:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
This will show the status of all pods created by the installer. If you see a pod enter a crash loop or hang in a non-ready state, you can view the pod’s log:
kubectl logs $POD_NAME --namespace $NAMESPACE_NAME
Upon successful installation, the following message appears:
<timestamp> INFO - fleetcommand_agent.Application - Deployment complete. Domino is accessible at $YOUR_FQDN
You can now access the application through HTTPS if you configure DNS for your fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) to point to an Ingress load balancer with the appropriate SSL certificates. The load balancer forwards traffic to your platform nodes.
Use Keycloak to enable user registration, so users can access your fresh Domino install. Keycloak is a user authentication service that runs on a pod in your cluster.