This topic describes how to connect to Snowflake from Domino.
The easiest way to connect to Snowflake from Domino is to create a Domino Data Source as described below.
You must have network connectivity between Snowflake and your Domino deployment.
To use Snowflake code integrations, such as Snowpark, you must agree to the Snowflake third party terms. To agree to these terms, you must have a Snowflake account with the ORGADMIN role. If you don’t have access to a Snowflake account with the ORGADMIN role, submit a Snowflake support ticket.
Domino recommends that you use a Domino Data Source to connect to a Snowflake instance from Domino.
-
From the navigation pane, click Data.
-
Click Create a Data Source.
-
In the New Data Source window, from Select Data Store, select Snowflake.
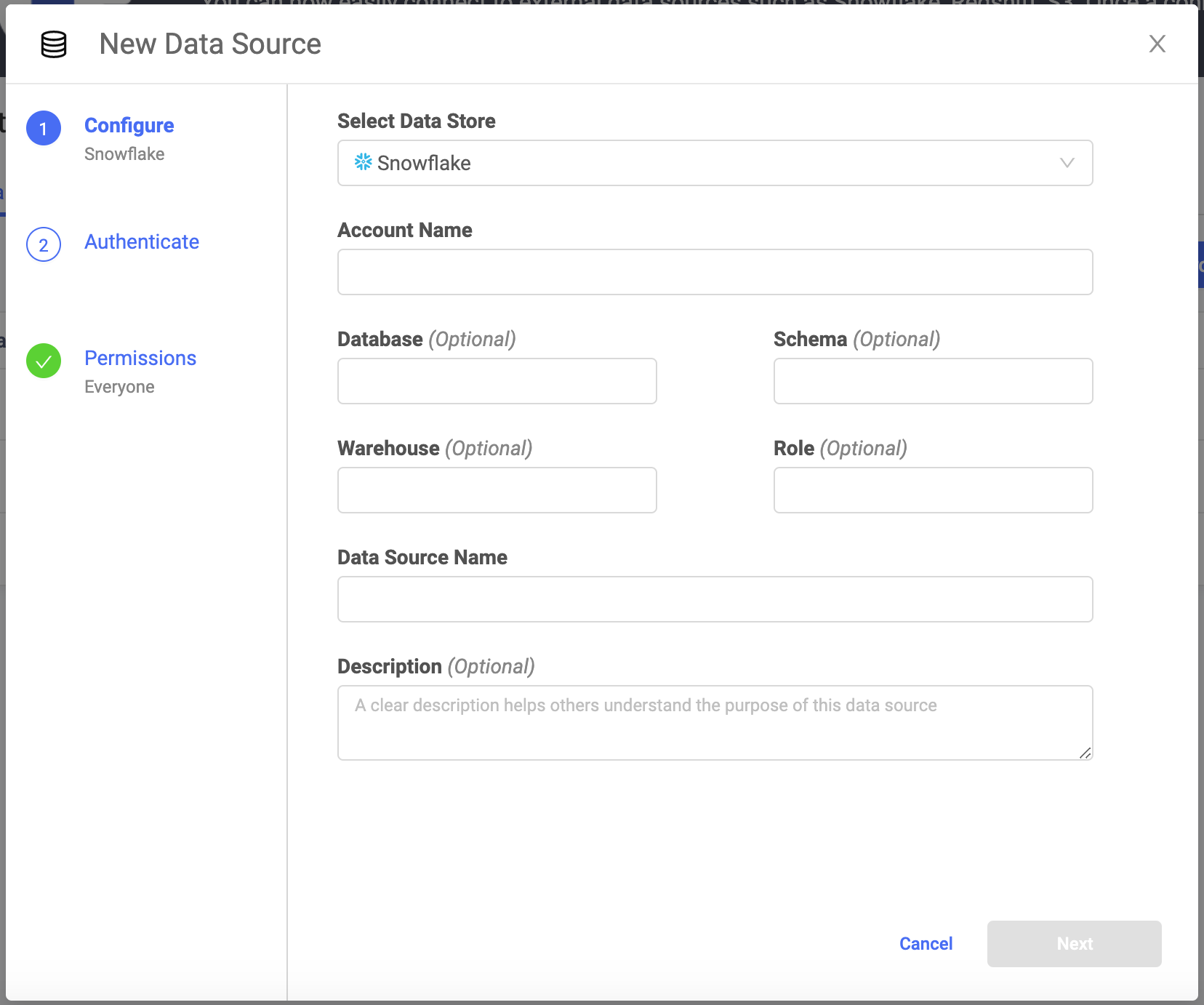
- Account Name
-
If the Domino deployment and Snowflake Data Source, are in the same region, enter the Account Name as
<account name>. However, if the Domino deployment and Snowflake Data Source are in different regions, enter the Account Name as<account name>.<region>. For example,abc.us-east. (For Azure, these might take the form ofdef.east-us-2.azure.) - Optional: Database
-
The name of the Snowflake database that contains the data.
- Optional: Schema
-
The name of the active schema for the session.
- Optional: Warehouse
-
The name of all the compute resource clusters that provide the resources in Snowflake.
- Optional: Role
-
The role that has privileges to the Data Source.
- Data Source Name
-
The name that identifies the Data Source.
- Optional: Description
-
The purpose for the Data Source.
-
Click Next.
-
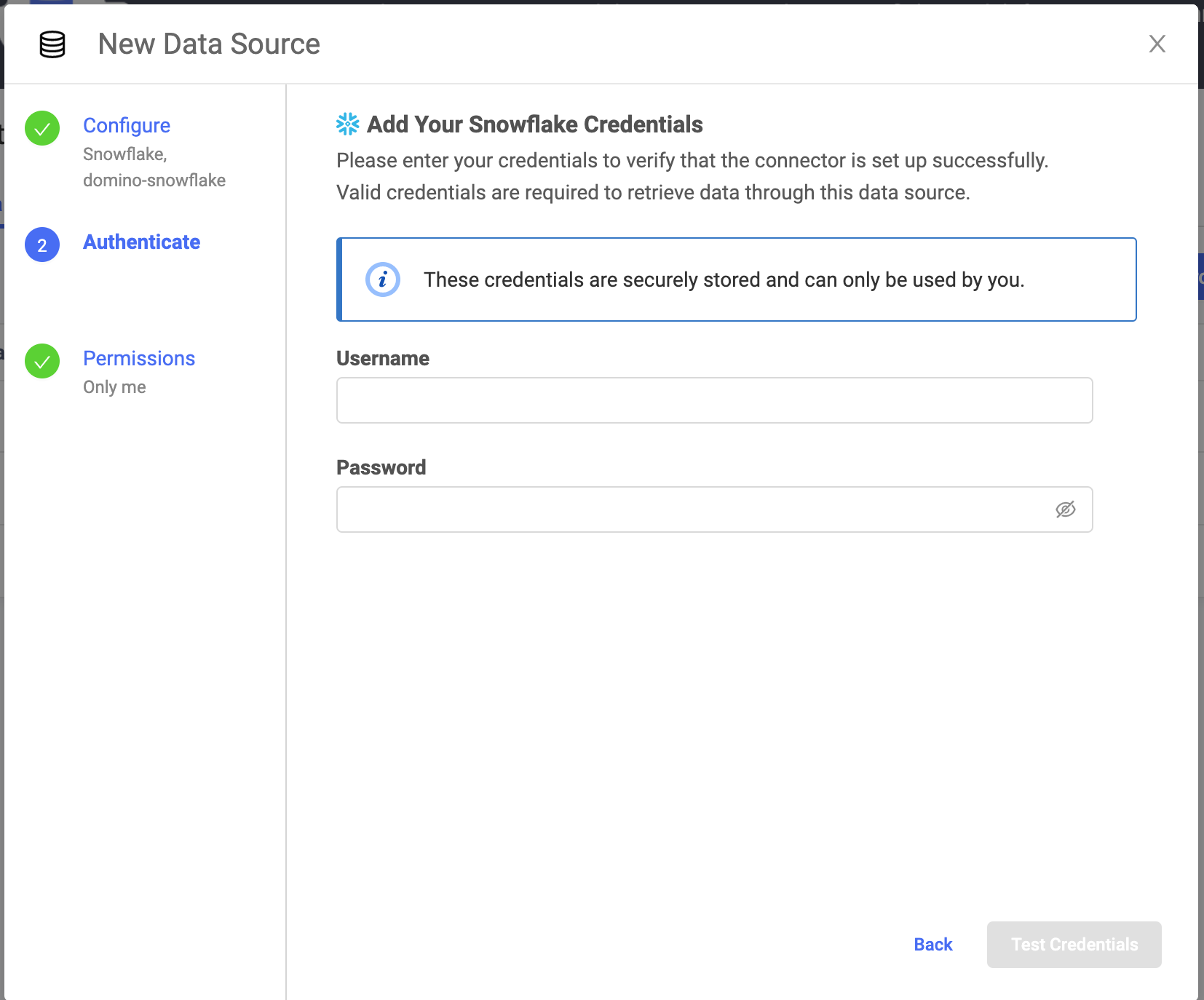
Enter the Username and Password to connect to Snowflake. Only basic (username/password) authentication is supported. The Domino secret store backed by HashiCorp Vault securely stores the credentials.
-
Click Test Credentials.
-
If the Data Source authenticates, click Next (or Skip for Now to configure authentication later).
-
Select who can view and use the Data Source in projects.
-
Click Finish Setup.
If your users have Domino permissions to use the Data Source and enter their credentials, they can now use the Domino Data API to retrieve data with the connector.
See Retrieve Data for more information.
|
Warning
| This section describes an alternate method to connect to the Snowflake Data Source. Domino does not officially support this method. |
-
Use the Snowflake Python connector (snowflake-connector-python).
-
Use the following Dockerfile instruction to install snowflake-connector-python and its dependencies in your environment.
USER root
RUN apt-get install -y libssl-dev libffi-dev && \
pip install -U pip && pip install --upgrade snowflake-connector-python
USER ubuntu+ If you encounter an error due to your Ubuntu version, use the following Dockerfile instruction:
+
USER root
RUN pip install -U pip && pip install --upgrade snowflake-connector-python
USER ubuntu-
Set the following Domino environment variables to store secure information about your Snowflake connection.
-
SNOWFLAKE_USER -
SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD -
SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNTSee Secure Credential Storage to learn more about Domino environment variables.
-
-
See Using the Python Connector for information about how to use the package. The following is an example.
import snowflake.connector import os # Gets the version ctx = snowflake.connector.connect( user=os.environ['SNOWFLAKE_USER'], password=os.environ['SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD'], account=os.environ['SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT'] cs = ctx.cursor() try: cs.execute("SELECT current_version()") one_row = cs.fetchone() print(one_row[0]) finally: cs.close() ctx.close()
Upload bulk data
The process for bulk uploads follows:
-
Write your dataframe into a .csv file.
-
Upload the .csv file to Snowflake into a table stage (or another stage).
-
Copy the data from the uploaded .csv file in the stage into the database table.
-
Delete the file from stage.
|
Note
| The columns in the table that the data will be copied into must be in the same order and have the same column names as the data in the file that was uploaded. You might want to create a temporary table and load the data to its destination as a follow-up step. |
For example:
# Note the use of a vertical bar (|) as separator instead of a comma
my_dataframe.to_csv('/mnt/results/my-data-file.csv', \
index=False, sep="|")
cs.execute("PUT file:///mnt/results/my-data-file.csv @%my_table")
sfStatement = """COPY INTO my_table
file_format = (type = csv
field_delimiter = '|' skip_header = 1)"""
cs.execute(sfStatement)You can also use generic Python JDBC or ODBC tools to connect to Snowflake. However, they are not specialized for use with Snowflake. They can have inferior performance and will require more time to set up.
See JDBC Driver and ODBC Driver for more information about JDBC and ODBC connections.
-
After connecting to your Data Source, learn how to Use Data Sources.
-
Share this Data Source with your collaborators.