This topic describes how to connect to Amazon Redshift from Domino. You must have network connectivity between Redshift and your Domino deployment.
The easiest way to connect to Redshift from Domino is to create a Domino Data Source as described below.
-
From the navigation pane, click Data.
-
Click Create a Data Source.
-
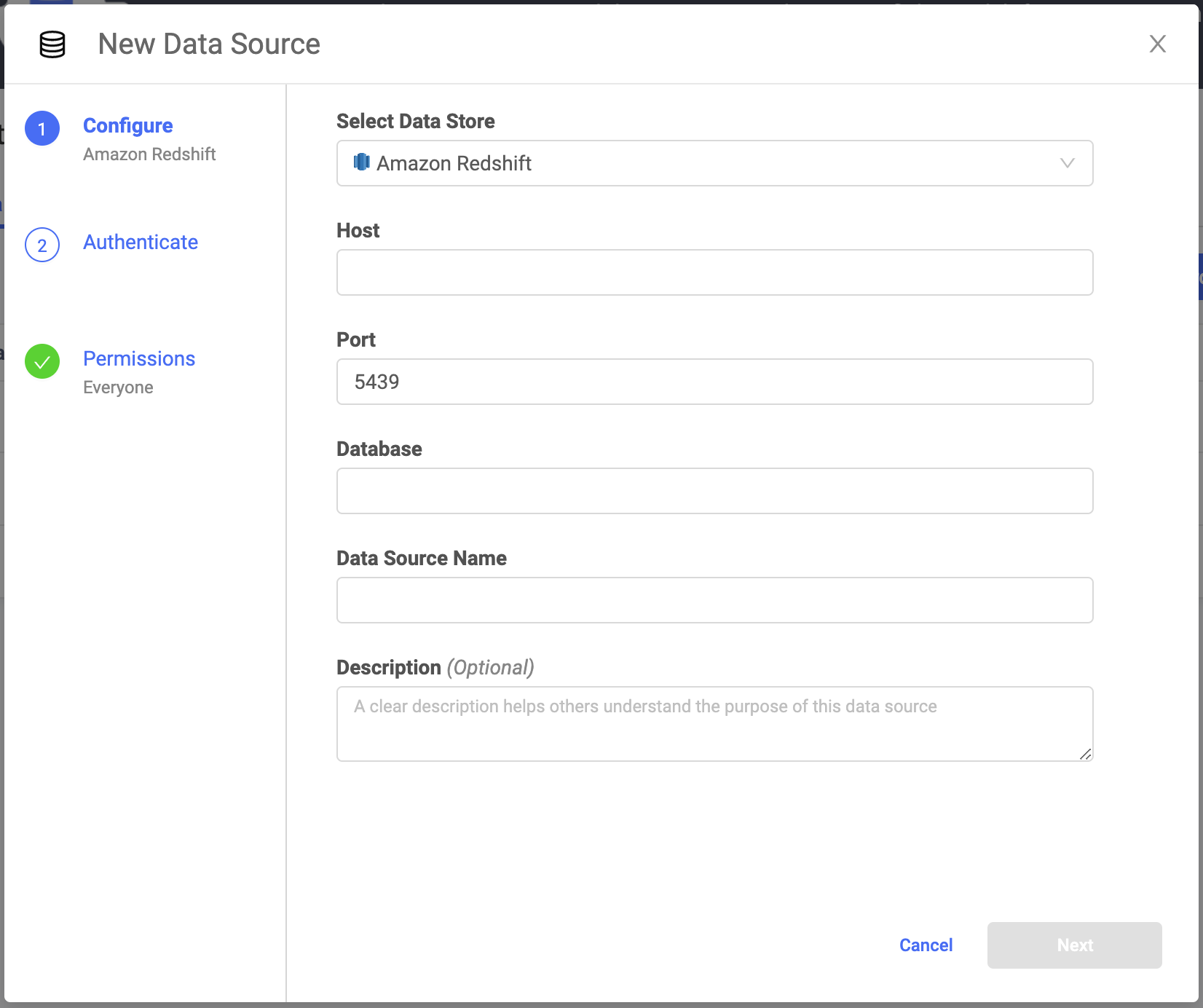
In the New Data Source window, from Select Data Store, select Amazon Redshift.
-
Enter the Host, Port, and name of the Database.
-
Enter the Data Source Name.
-
Optional: Enter a Description to explain the purpose of the Data Source to others.
-
Click Next.
-
Enter the Username and Password to connect to Amazon Redshift. Only basic (username/password) authentication is supported. The Domino secret store backed by HashiCorp Vault securely stores the credentials.
-
If the Data Source authenticates, click Next.
-
Select who can view and use the Data Source in projects.
-
Click Finish Setup.
|
Warning
| This section describes an alternate method to connect to the Redshift Data Source. Domino does not officially support this method. |
Prerequisites
-
Domino recommends storing your database username and password as environment variables in your project. This lets you access them at runtime without including them in your code.
Python
To establish a connection to Redshift with the psycopg2 library:
import psycopg2
import os
HOST = os.environ['REDSHIFT_HOST']
PORT = 5439 # redshift default
USER = os.environ['REDSHIFT_USER']
PASSWORD = os.environ['REDSHIFT_PASSWD']
DATABASE = 'mydatabase'
def db_connection():
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host=HOST,
port=PORT,
user=USER,
password=PASSWORD,
database=DATABASE,
)
return conn
example_query = "SELECT * FROM my_table LIMIT 5"
conn = db_connection()
try:
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(example_query)
results = cursor.fetchall() # careful, the results could be huge
conn.commit()
print results
finally:
conn.close()
# using pandas
import pandas as pd
conn = db_connection()
try:
df = pd.read_sql(example_query, conn)
df.to_csv('results/outfile.csv', index=False)
finally:
conn.close()R
To establish a connection to Redshift with the RPostgreSQL library:
install.packages("RPostgreSQL")
library(RPostgreSQL)
redshift_host <- Sys.getenv("REDSHIFT_HOST")
redshift_port <- "5439"
redshift_user <- Sys.getenv("REDSHIFT_USER")
redshift_password <- Sys.getenv("REDSHIFT_PASSWORD")
redshift_db <- "mydatabase"
drv <- dbDriver("PostgreSQL")
conn <- dbConnect(
drv,
host=redshift_host,
port=redshift_port,
user=redshift_user,
password=redshift_password,
dbname=redshift_db)
tryCatch({
example_query <- "SELECT * FROM my_table LIMIT 5"
results <- dbGetQuery(conn, example_query)
print(results)
}, finally = {
dbDisconnect(conn)
})-
After connecting to your Data Source, learn how to Use Data Sources.
-
Share this Data Source with your collaborators.