Domino supports importing Git repositories to projects. When you add a repository to a project, it is available to Runs that you start in the project. This means you can access the contents of the repository, just as you would your Domino files.
This topic explains how you can import a Git repository to a project, access the repository from within a Workspace, and commit changes back to the repository.
Domino supports connecting to Git servers through HTTPS and SSH for both public and private repositories.
|
Note
|
If you want to use Git with the Git service provider of your choice, Domino recommends that you use Git-based Projects. |
If you are adding a private repository, want to write commits to remote, or are using SSH, you must add Git credentials to your Domino account. Domino uses these credentials to authenticate with the service hosting your repository when you start a Run.
Domino stores the following types of credentials:
-
Personal Access Tokens
-
SSH private keys
-
Username and password
Option 1: SSH key creation
To connect with SSH, you must have a private SSH key that corresponds to a public key that you’ve added to your Git service. See the GitHub documentation for instructions about how to create and add keys.
Option 2: Personal Access Token creation
You must have a Personal Access Token to access a private repository through HTTPS. You must have a Personal Access Token if the URI you want to use to interact with a repository is formatted as:
https://<domain>/<user>/<repository>.gitPersonal Access Tokens are supported by the following Git services.
-
GitHub Personal Access Tokens: The minimum scopes to grant for full functionalities are
repoandread:user
-
GitLab Personal Access Tokens: The minimum scopes to grant for full functionalities are
read_api' and `write_repo. If you are creating Git-based projects and plan to create a repository from Domino, you must grantapiaccess to the Personal Access Token.
To connect to Bitbucket repositories through HTTPS from Domino, you must add a Bitbucket App Password credential to your Domino account.
If your GitHub organization requires SSO then you must authorize the PAT or SSH key to access private repositories through Domino.
See the GitHub documentation for instructions about authorizing keys for SSO on Github.
Option 1: SSH private key
You must have a SSH Private Key to access a repository through SSH. You must have a SSH private key if the URI you want to use to interact with a repository is formatted as:
<user>@<domain>:<username>/<repository>.git
SSH access is supported by the following Git services.
After setting up SSH access with your Git service, you will have a public key that you provided to the Git service, and a private key. Use these steps to add the private key to Domino:
-
Copy your SSH key.
From a terminal, run
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsato copy the key to your clipboard, ir you set up your key with the standard name and in the standard location.If you copy the key manually, remember to include the
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----and-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----header and footer. -
In the navigation pane, click your username, then click Account Settings.
-
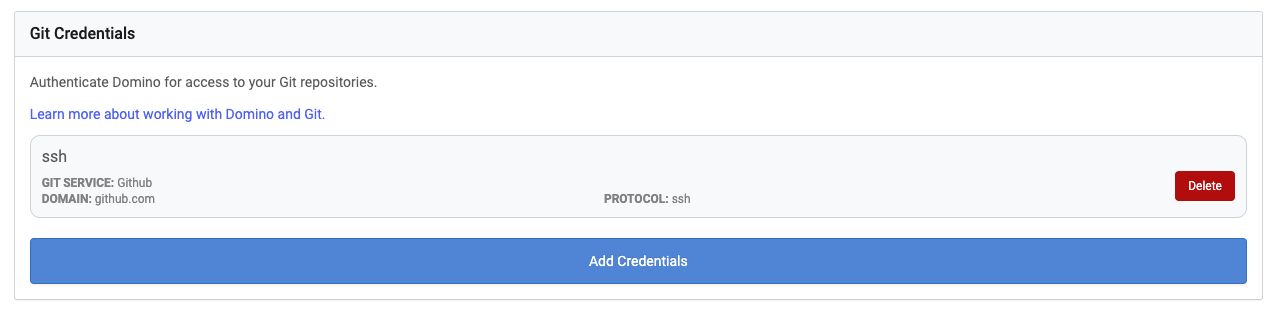
Go to Git Credentials, then click Add a New Credential.
-
In Domain, enter the exact domain of the service hosting your repository, such as
github.com,bitbucket.com, oryour-internal-gitlab-url.com. -
For Authentication Credential Type, click Private SSH Key.
-
Paste your private key. This is the contents of the private key file that matches the public key you provided to your Git service.
-
If you set up your SSH keys to require a passphrase when used, enter it in the Passphrase field, then click Add Credentials. Your credential is listed in Git Credentials.
Option 2: Personal Access Token
After generating a Personal Access Token in your Git service, use these steps to add it to Domino:
-
In Domino, click your username, then click Account Settings.
-
Go to Git Credentials, then click Add a New Credential.
-
In the Domain field, enter the exact domain of the service hosting your repository, such as
github.com,bitbucket.com, oryour-internal-gitlab-url.com. -
For Authentication Credential Type, click Personal Access Token.
-
Enter your Personal Access Token, then click Add Credentials. Your credential is listed in Git Credentials.

-
Open the project to which you want to add a repository, then click Files.
-
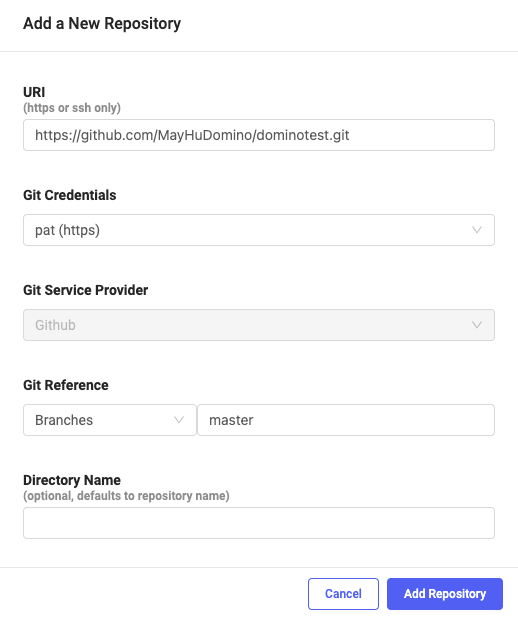
Click to open the Git Repositories tab, then click Add a New Repository.
-
Enter a directory name and the HTTPS or SSH URI of the repository you want to add. The directory name will be the directory in
/reposthat this repository clones into. It defaults to the name of the repository. -
Select the branch of the repository that you want Domino to check out when it clones this repository into a run or workspace. If you leave this setting at Use default branch, Domino will check out the branch specified as default by your Git service, typically
master. You can also specify a different branch name, tag name, commit ID, or supply a custom Git ref. -
Click Add Repository.
When you start a run or workspace in a project, any repositories added to the project are cloned into /repos and will have the branch or commit you specified checked out.
Remember that your Domino working directory is in /mnt, which is a sibling of /repos.
Both directories are in the filesystem root (/).
Scripts you have added as Domino files can interact with the contents of these repositories by specifying an absolute path to /repo-name>/<file>.
Commit back to Git repositories
When you start a Workspace session in a project that has added Git repositories, you will see those repositories listed in the Session Overview under Git repos. If you make changes to the contents of those repositories while running the workspace, those changes will be itemized file-by-file under each repository.
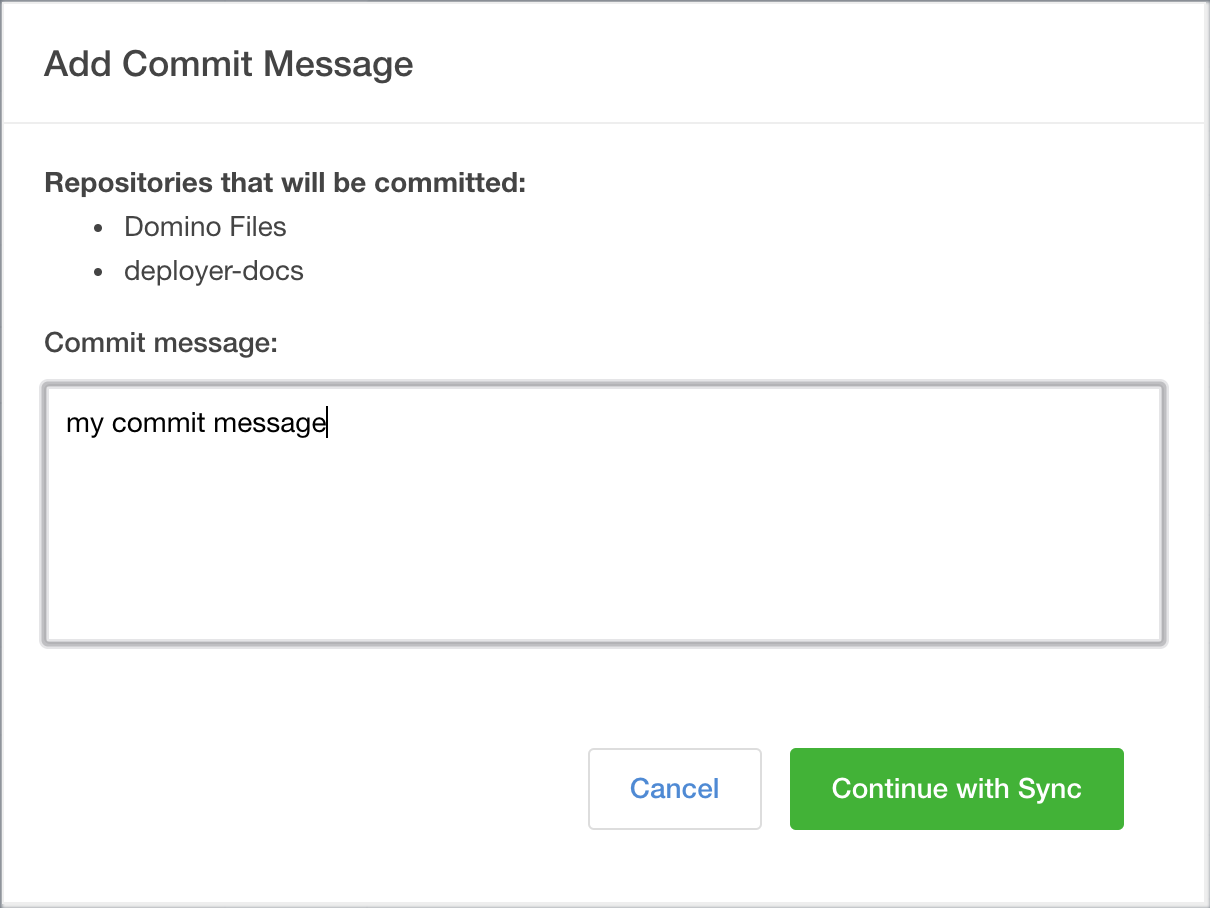
If you want to commit those changes back to the repository, select the check box next to the repository name and then click Full Sync.
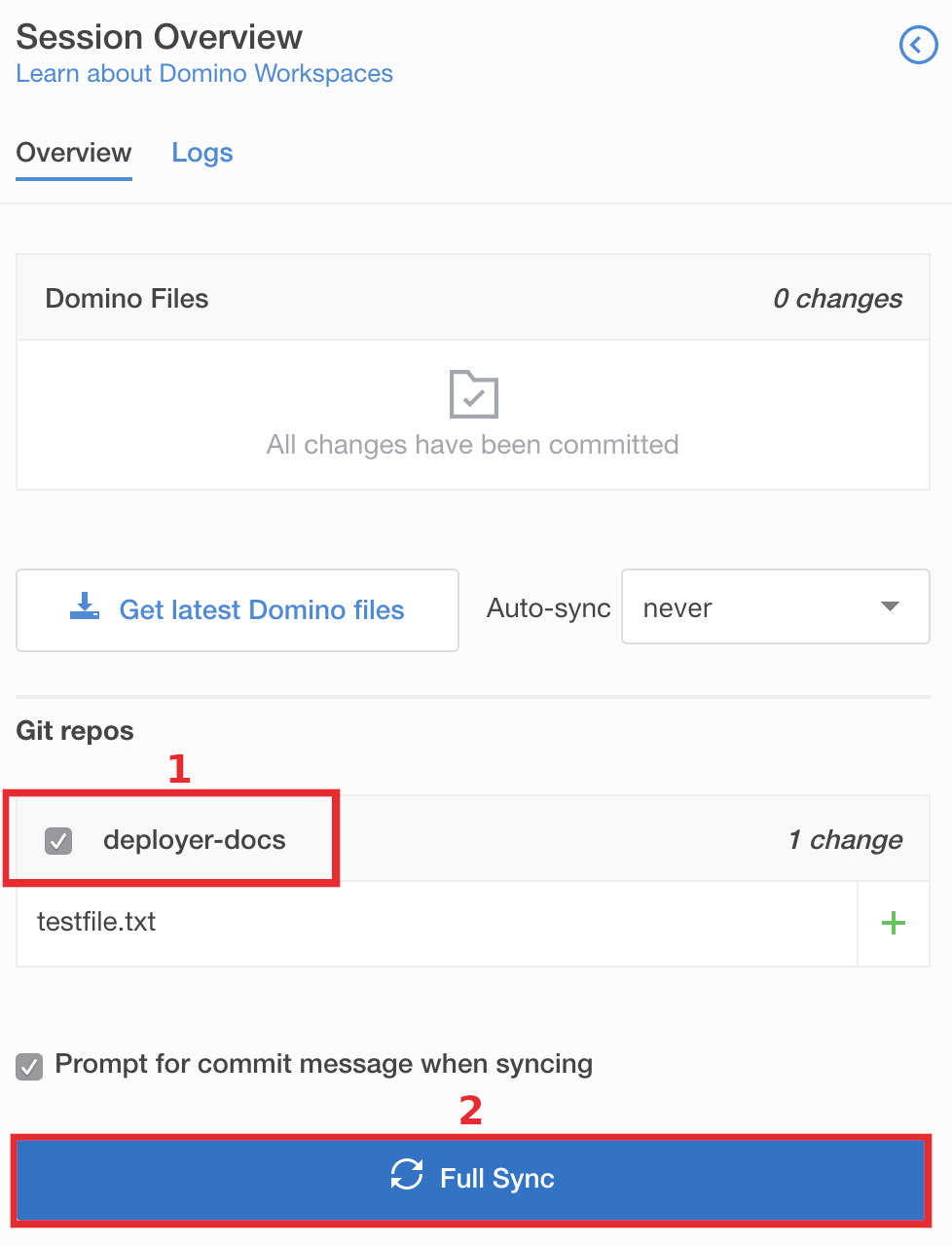
Enter a commit message. This commit message is attached to commits to the selected Git repositories, and to a new revision of the Domino project if there are changes to Domino files. Git commits are pushed to the default branch you specified when adding the repository.
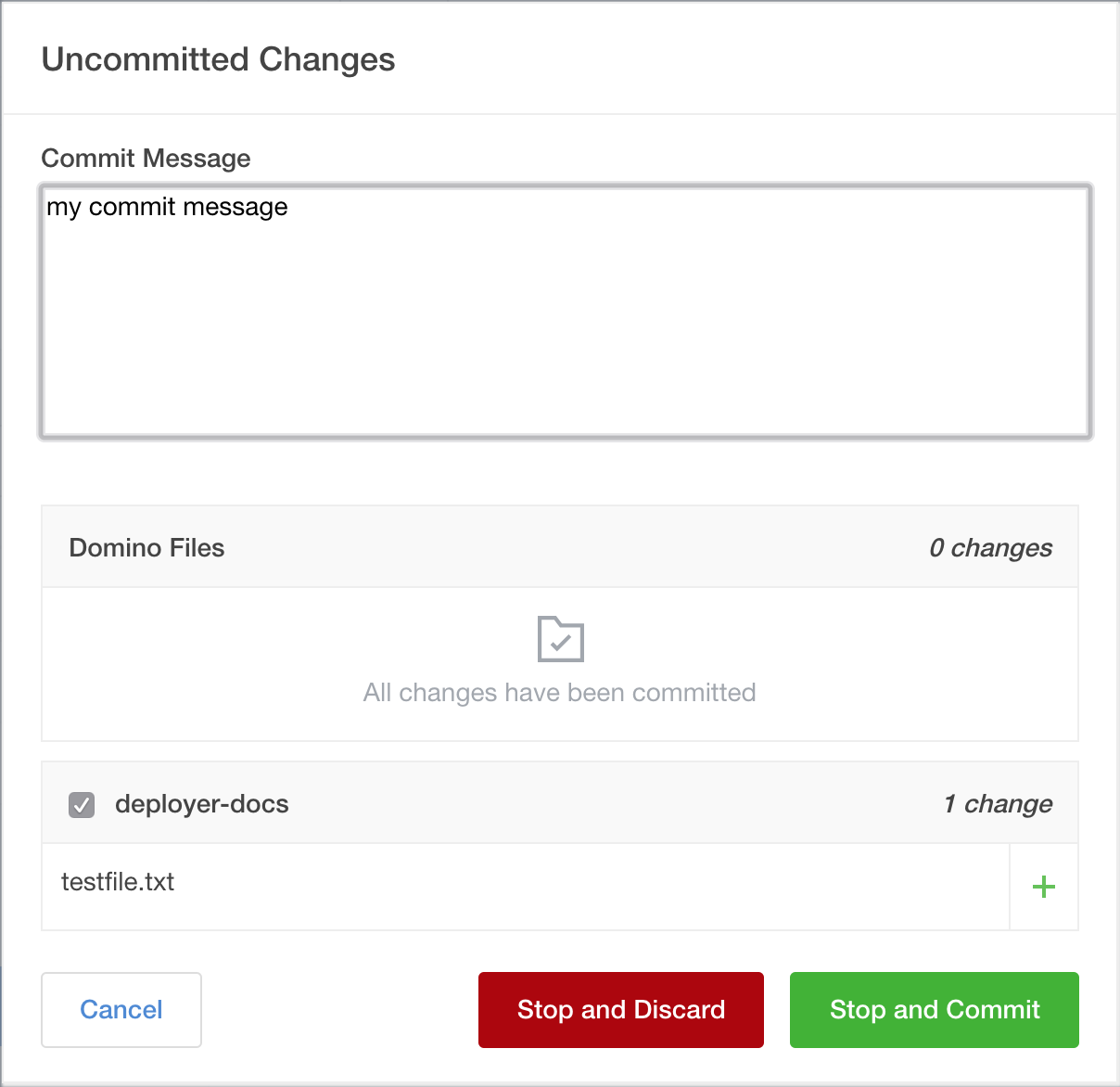
If you attempt to stop your Workspace while there are uncommitted changes to your Git repositories, you are prompted to commit those changes. This works the same as the Session Overview page. Select the check box next to the repositories you want to commit to, enter a commit message, and click Stop and Commit.
If you try to commit when there are conflicts between your local changes and the state of the default branch in remote, Domino creates a new branch from its local state. Domino will then push that new branch to remote.
After this happens, you must resolve those conflicts outside of Domino, or use the command line in your Workspace session to resolve them. The next time you launch a Workspace session, Domino will check out the default branch from remote, not the new branch it pushed.
Git interaction from the Workspace command line
Both Jupyter and RStudio workspaces have command line tools.
You can use these to interact with your repositories with conventional Git commands.
Go to /repos in your command line to find your project’s repositories.
See the official Git documentation to learn more about using Git on the command line.
To open the RStudio command line, click Tools > Shell….
To open the Jupyter command line, from the Files tab click New > Terminal.
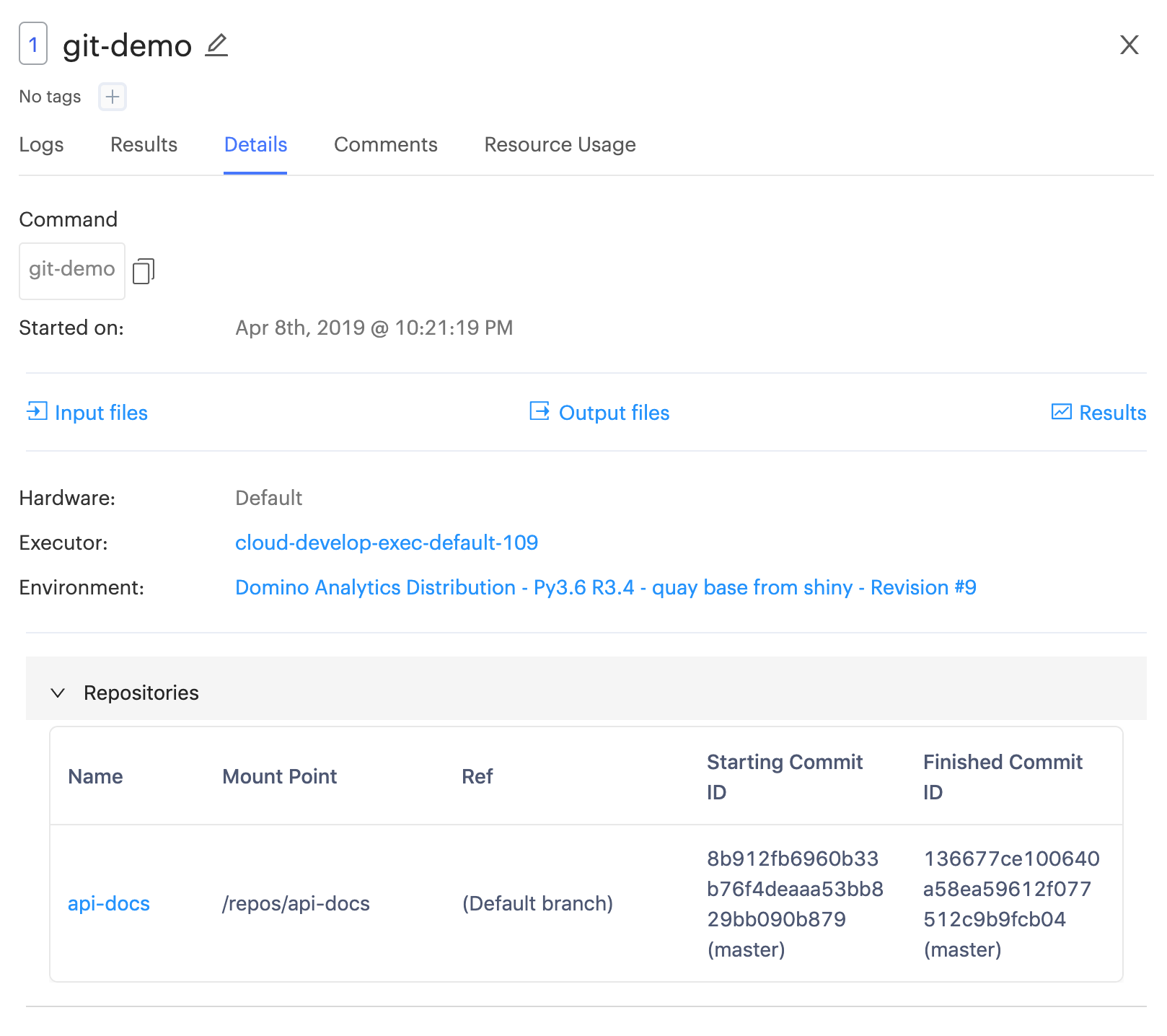
When viewing the Details tab of a Domino Run, at the bottom you will find a Repositories panel. You can expand this panel to see details of how the repository changed during the Run. Domino records the checked out commit at the start of the Run and the end of the Run.
Run Error:
Errors occurred while processing dependencies. Contact support@dominodatalab.com:
Credentials are required for your repository: project-name (ssh://git@github.com/your-org/projectname.git)Solution:
Your Git Credential added to Domino might have the incorrect Domain. Double-check the domain field in your Git credential to ensure it matches your exact Git repository URL, like:
-
github.com -
bitbucket.com -
your-internal-gitlab-url.com
Run Error:
Errors occurred while processing dependencies. Contact support@dominodatalab.com:
Authentication is required for your repository:
The repository provided requires credentials but none were found.
Add SSH or PAT authentication to your Domino account.Solution:
There are a couple steps to check when encountering this error. First, ensure your private SSH key or PAT has been added to the Git Credentials section of your Domino Account Settings page. Second, if your organization’s Git repository requires SSO access, you may need to authorize the key you have added. See Authorizing an SSH key for use with SAML single sign-on for more details.
Run Error:
Errors occurred while processing dependencies. Contact support@dominodatalab.com:
remote: Invalid username or password.
fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://github.com/<your account>/<your repo>/'Solution:
If your organization’s Git repository requires SSO access, you may need to authorize the key you have added. See Authorizing an SSH key for use with SAML single sign-on for more details.