Data is at the core of every data science project. Data varies across different use cases and lives in many places within an organization. Domino provides the flexibility to access all of your data, whatever and wherever it may be.
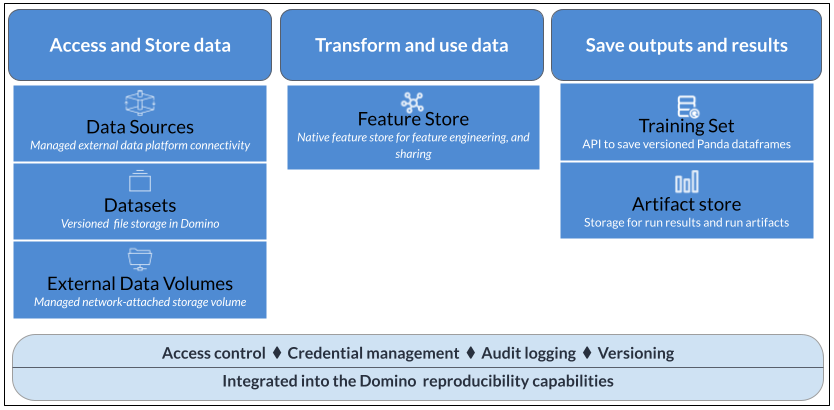
Each of these data access and storage mechanisms comes with pros and cons, suited to different use cases. The topics in this section explain how to connect your data to Domino and use it in your projects.
Domino provides a single interface for accessing all of your data, wherever it lives.
Domino Data Source Connectors provide easy setup for connections to popular data services, or you can connect Domino directly to any data service using the same code you use in your local environment. Domino Datasets enable you to upload, store and manage data within the Domino system.
You can also mount external storage volumes to Domino and use your Git repositories as project file stores.
The following table compares Domino’s data access and storage methods:
| Domino Datasets | Data Source connectors | External Data Volumes | Project artifacts | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Description | Read/Write managed folders shareable within Domino. Can be versioned with snapshots for reproducibility. | Managed data connectors that can connect to SQL and file-type stores. Or, connect directly to any data service using a library. | Managed external file store mounts. | A special, version-controlled folder that works similarly to Git LFS. |
Location | Network File System (NFS) storage or Amazon Elastic File System | Any external data service | NFS or Server Message Block (SMB) storage | Domino File System (DFS) |
Intended use cases |
| Accessing data in existing external stores such as databases | Exposing existing IT data storage interfaces within Domino | Storing outputs (such as charts, serialized model files, output CSVs, and so on) |
Intended data sizes | Up to ~1TB per Dataset and hundreds of TB across Datasets | Constrained only by what you query and pull into the machines executing your code | Constrained by your existing network storage | Up to ~10GB |
Advantages | Supports much larger data than project artifacts, with snapshots for reproducibility. | Connectors provide an easy and secure way to connect to external data without drivers or configuration. Direct connections use the same code you would use outside of Domino, with the flexibility to access files or data however you want. | Use the same code you would use outside of Domino. | Simple to use and share. |
Limitations | Snapshots must be managed to minimize storage costs. | Code for accessing connector-supported data sources is not portable outside Domino. Domino does not automatically track snapshots for reproducibility. | Will not automatically track snapshots for reproducibility. | Not performant at scale of data size or many thousands of files. |
Query methods | Path to the mounted Dataset |
| Path to the mounted volume and files | Path to the project’s files |
Supported executions |
|
|
| All |
Access control |
| Based on Domino user/organization as configured by an admin | Per-project collaborator permissions |
Domino’s feature store enables you to create, publish and share features to a global registry for others to discover and reuse. It leverages the Feast open-source feature store library with additional capabilities around ease of installation, feature cataloging, search and re-use.
See Publish and reuse features for details.
When your project requires reproducible data, you can create Dataset snapshots that are immutable and versioned. You can also use the Data API to create training sets based on any of your data in any location. If your external data sources or network filesystems support dataframes, snapshots, or versioning, you can use those features in your code in Domino.
Data in Domino is reusable across multiple projects, with full control over who can access it. You can share data with your collaborators and decide who has read-only access or the ability to edit the data.
See Data security and sharing to learn how to share your data with collaborators and keep it secure.