There are two strategies to working with data in Domino:
-
You can copy your data into Domino
If you are working with data that is on your local machine or in a shared server, you might want to upload your data into Domino.
-
You can query your data from Domino
If you have a large dataset stored in a database or data service, you might just have to query the database or the API for the data service.
In this step, you’ll copy your data into the project using the Jupyter terminal. If you have not done so, complete Step 3 to start a Jupyter workspace.
The starting file path in your Jupyter workspace is /mnt. By default,
this is considered the root of your Domino project. If you add or modify
files in /mnt, you can save them back to your project when you stop or
sync the workspace.
-
Go to New > Terminal to open a Jupyter terminal.
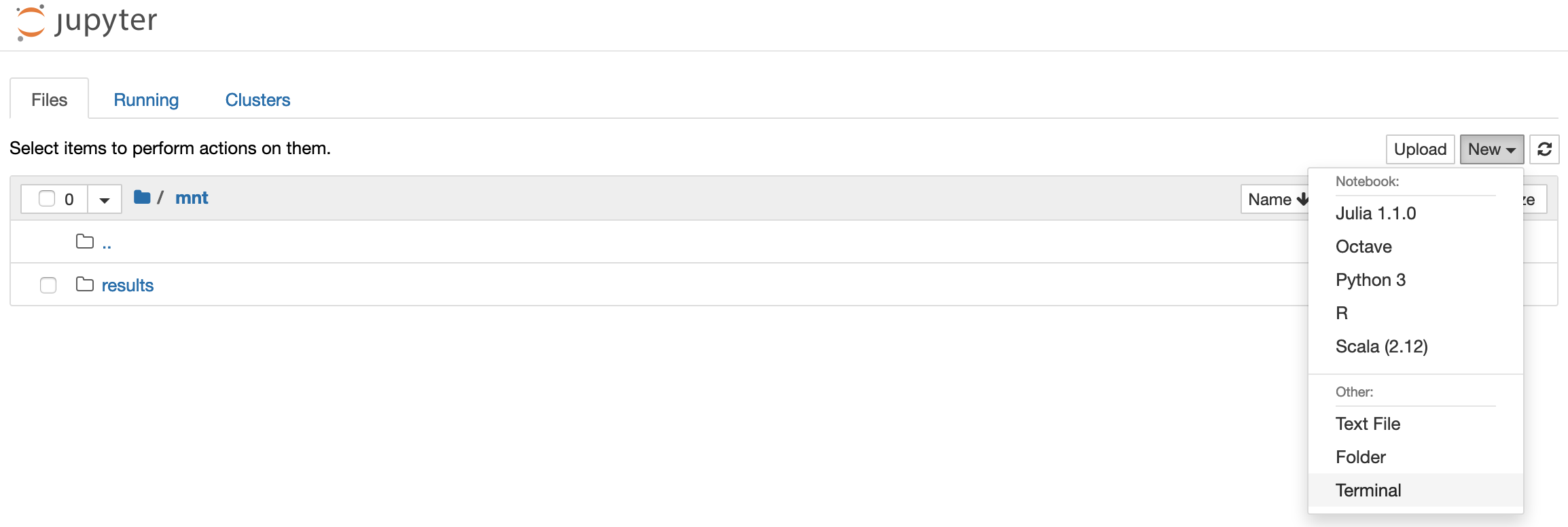
-
In the new terminal, run the following command to fetch some data from the BMRS:
curl -o data.csv "https://www.bmreports.com/bmrs/?q=ajax/filter_csv_download/FUELHH/csv/FromDate%3D2020-01-01%26ToDate%3D2021-01-01/&filename=GenerationbyFuelType_20191002_1657" -
In the File Changes tab of your workspace, type a commit message in the text box.
-
Click Sync All Changes to synchronize the information and save
data.csvto your Domino project.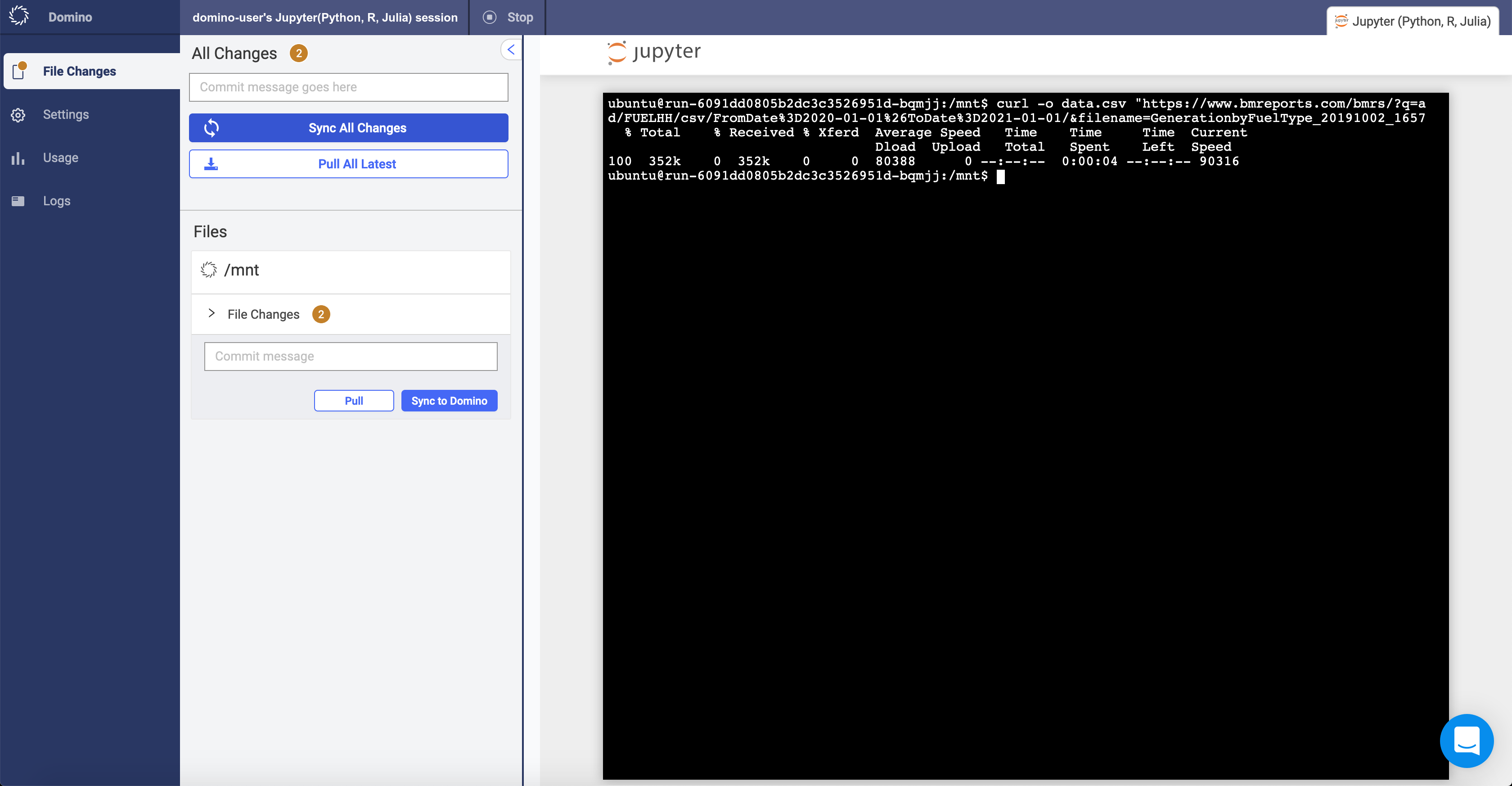
-
Stop the workspace.
-
Click the Domino logo to return to your project in Domino. In the navigation pane, click Files. The raw data is saved in the latest revision.