Create an on-demand Spark cluster with the desired cluster settings attached to a Workspace or Job.
-
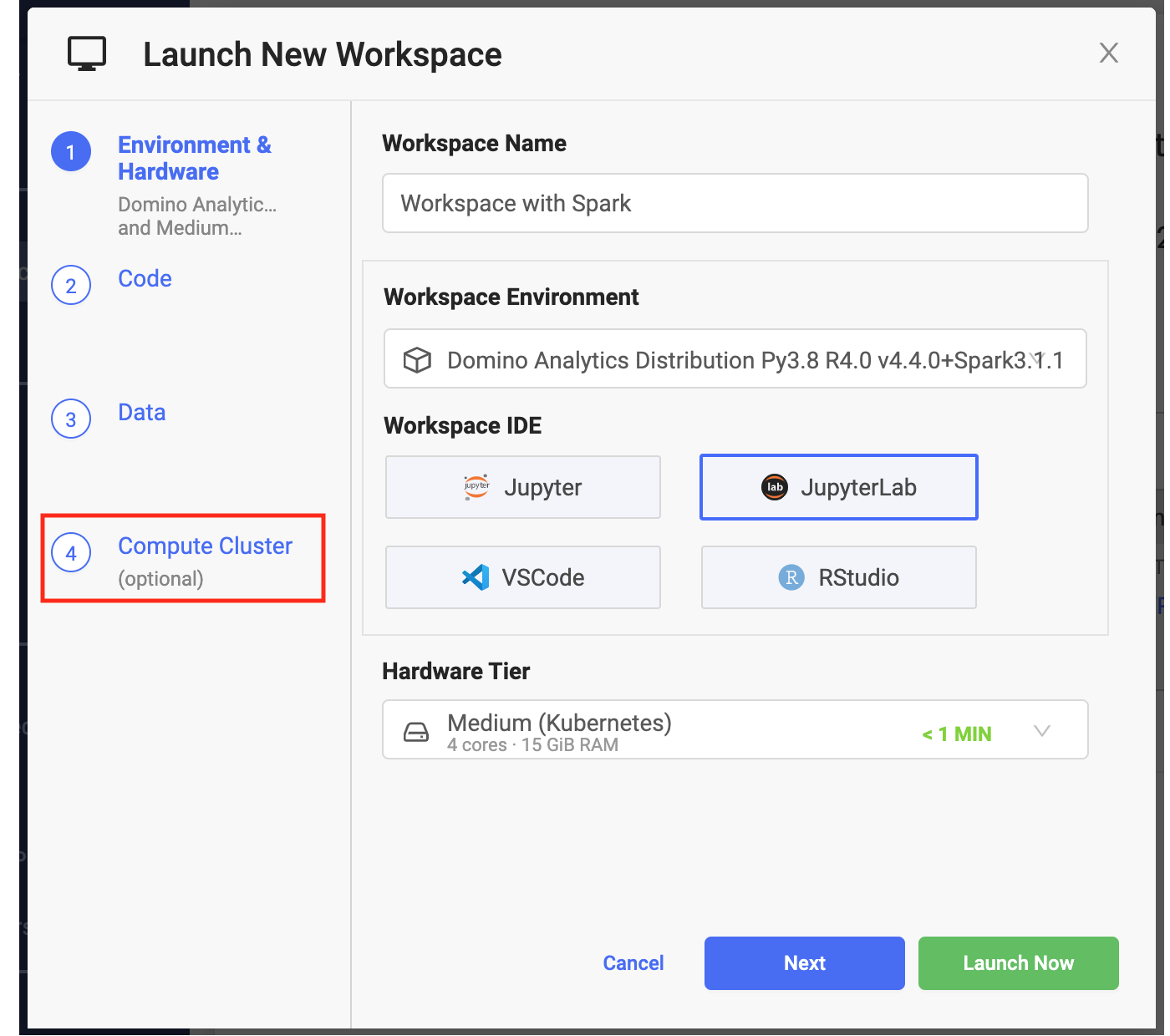
Click New Workspace.
-
From Launch New Workspace, select Attach Cluster.
-
Specify the cluster settings and launch you workspace. After the workspace is running, it has access to the Spark cluster you configured.
The hardware tier for your workspace determines the compute resources available to your Spark driver process.
-
From the Jobs menu, click Run.
-
From Start a Job select Attach Cluster.
-
Specify the cluster settings and launch your job. The job has access to the Spark cluster you configured.
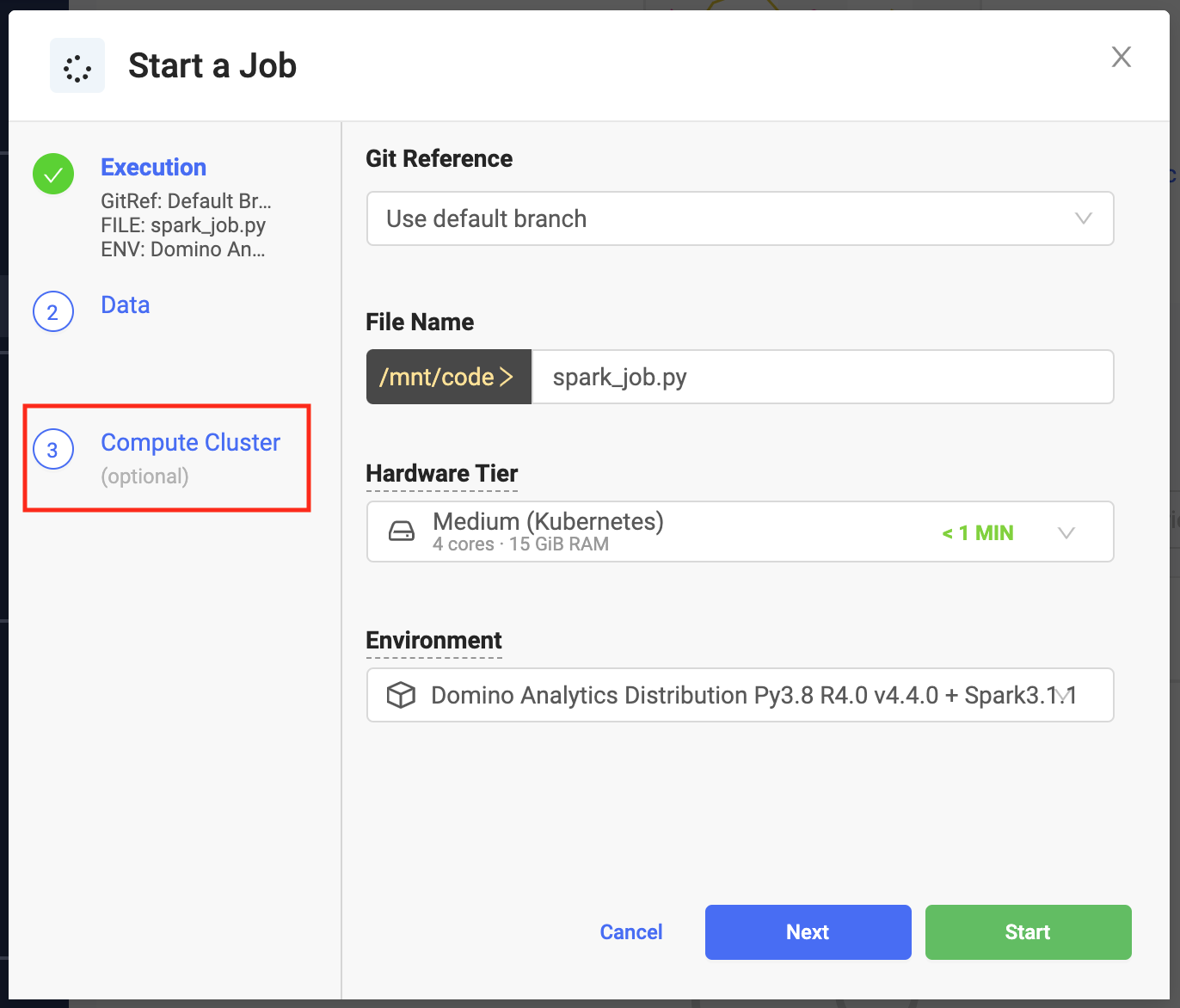
You can use any Python script that contains a PySpark job.
You can also use spark-submit to submit jobs. However, this is not recognized automatically as a Domino supported job type, so you must wrap it with a shell script unless you included a copy of spark-submit.sh when you prepared your compute environment.
The following is an example of a simple wrapper my-spark-submit.sh.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
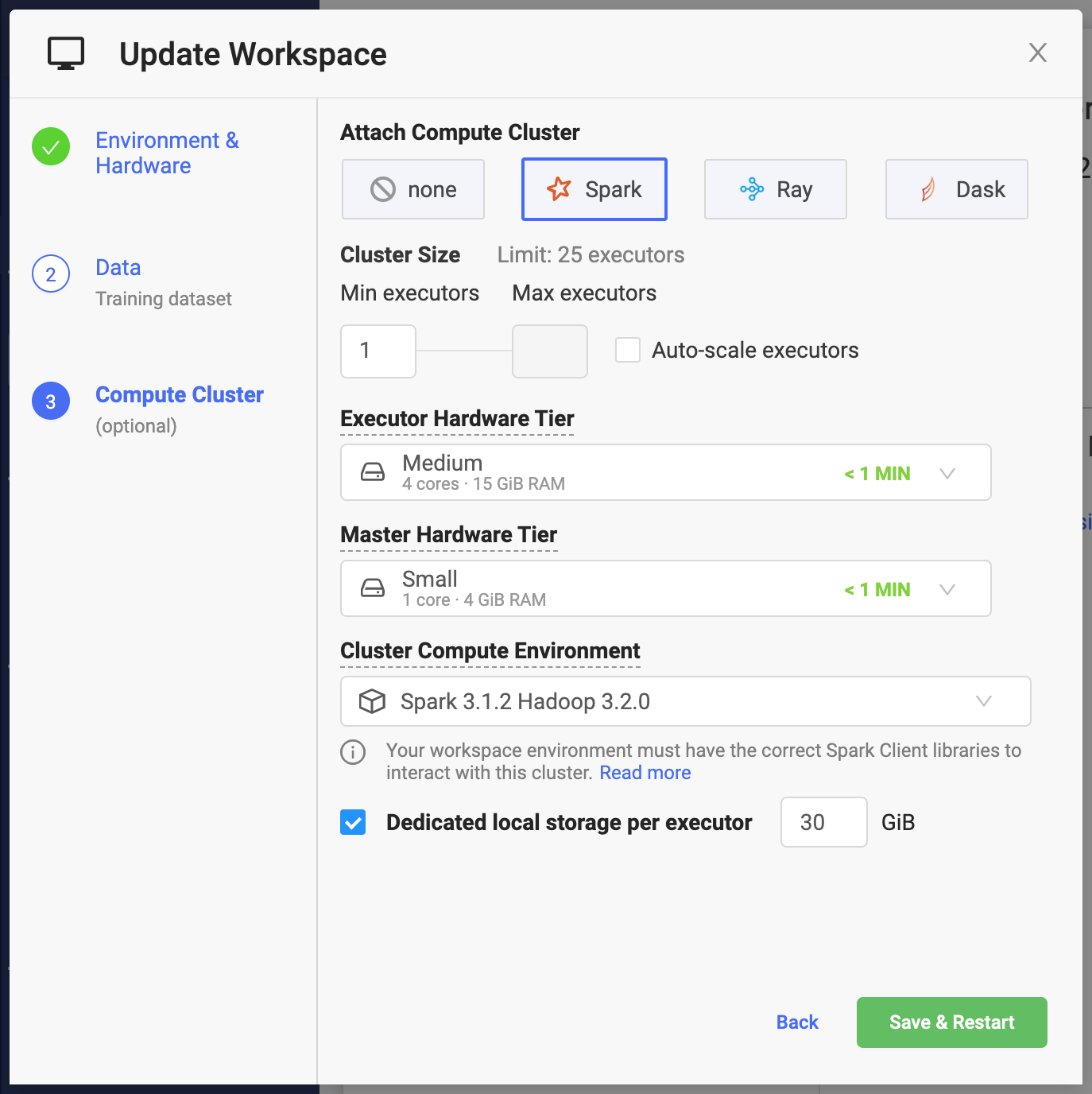
spark-submit $@Domino makes it simple to specify key settings when creating a Spark cluster.
-
Number of Executors
Number of Executors that will be available to your Spark application when the cluster starts. If Auto-scale workers is not enabled, this will always be the size of the cluster. The combined capacity of the executors will be available for your workloads.
When you instantiate Spark context with the default settings, the
spark.executor.instancesSpark setting is set to the number specified in the previous window.